New concussion guidelines for team physicians
- Created on Sunday, 01 April 2012 20:27
- Last Updated on 16.01.2013
- Published Date
 INDIANAPOLIS – Team physicians who assess and treat athletes suspected of concussion have new guidelines from the American College of Sports Medicine (ACSM), according to a team physician consensus statement just released. Under no circumstances should an athlete suspected of, or diagnosed with, a concussion return to play the day of their injury.
INDIANAPOLIS – Team physicians who assess and treat athletes suspected of concussion have new guidelines from the American College of Sports Medicine (ACSM), according to a team physician consensus statement just released. Under no circumstances should an athlete suspected of, or diagnosed with, a concussion return to play the day of their injury.
“There is to be no same-day return-to-play after a concussion, even if the athlete’s initial symptoms resolve as the athletic event or practice progresses,” said Stanley A. Herring, M.D., FACSM, chair of the writing group and one of the team physicians for the Seattle Seahawks and Seattle Mariners. “Also, the subsequent decision to return an athlete to play should be individualized, not based on a rigid timeline or solely on the demands of a particular sport.”
The team physician consensus statement, titled “Concussion (Mild Traumatic Brain Injury) and the Team Physician: A Consensus Statement – 2011 Update,” updates recommendations made in 2006. While advising against same-day return-to-play is the biggest change from the 2006 statement, there are other changes team physicians should note.
- Physicians should use standardized concussion assessment tools, such as the NFL Baseline and Sideline Tools, for pre-season and post-injury evaluation. Neurological assessments should emphasize cognitive function, cranial nerve and balance testing.
- Physicians should use the preseason to develop an emergency medical action plan, including a specific plan for concussion management, and they should also assemble a concussion management team.
- Neuropsychological (NP) testing is one component of the evaluation process, and it should not be used as a stand-alone tool to diagnose, manage or make return-to-play decisions in concussion.
- Tests using event-related and evoke-related potentials, as well as tests using biomarkers, have been inconclusive in identifying individuals with concussions; however, they may one day be applicable.
- Physicians should understand their states’ laws regarding concussion as well as the rules and regulations from their sports’ governing bodies.
“There are more than 3.8 million concussions suffered in sports and recreational activities each year,” said Herring. “Proper management by team physicians is crucial because it can mitigate potentially life-threatening complications.”
Before returning to play, an athlete should have no symptoms (at rest or with cognitive effort), should not be taking any medications to mask concussion symptoms and should be back at baseline with their neurological examinations and NP testing if available. The process may take days, weeks or months, and the recurrence of symptoms should warrant additional rest and monitoring.
A concussion is a brain injury resulting from linear (the brain directly hitting the skull) or rotational (the brain swirling forcefully in the skull) accelerations following impact. Concussions occur in helmeted and non-helmeted sports, and they are most common in football, ice hockey, soccer and lacrosse.
“Concussion (Mild Traumatic Brain Injury) and the Team Physician: A Consensus Statement – 2011 Update” was a collaboration among ACSM, the American Academy of Family Physicians, the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, the American Medical Society for Sports Medicine, the American Orthopaedic Society for Sports Medicine and the American Osteopathic Academy of Sports Medicine.
The team physician consensus statement is published in the December 2011 issue of Medicine & Science in Sports & Exercise®, the official journal of ACSM.
Brain Health
It is rare for a sports-related concussions to result in a more serious injury such as a skull fracture or hematoma. Nonetheless, it pays to be aware that catastrpohic injuries do sometimes occur as ...
read more...-
CT scans may increase brain cancer risk
Children and young adults scanned multiple times by computed tomography (CT), a commonly used dia...
-
Sub-concussive impacts may affect learning
MINNEAPOLIS – A new study suggests that head impacts experienced during contact sports such as ...
-
Physical activity boosts learning
INDIANAPOLIS – School administrators looking to restructure the academic schedule should consid...


Neuroscience
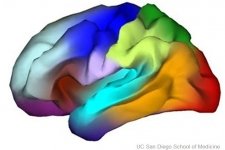
Athens, Ga.- University of Georgia researchers have developed a map of the human brain that shows great promise as a new guide to the inner workings of the body's most complex and critical organ.
...
read more...-
Does CTE infect neuron to neuron?
NFL Hall of Famer "Iron Mike" Webster's life ended in 2002 when he suffered a heart attack at age...
-
Progesterone seems to protect neurons after injury
It is not yet known why girls suffer concussions at a higher rate than boys. The most prevalent...
-
Amino acids may restore concussion's chemical imbalance
Concussions are often called the "invisible" injury because they are usually not detectable by t...
Resources
- School professionals play an important role in the health of all students. Recognizing the signs and symptoms of concussion is important, as is managing their return to school ...
- CDC's Concussion Training for Clinicians
-
Concussion Education Video Programs - Free and Easy
Parents, athletes, coaches and medical professionals have access to concussion education created...
-
New concussion guidelines for team physicians
INDIANAPOLIS – Team physicians who assess and treat athletes suspected of concussion have new ...
quick links
Latest News
Concussions Occur...
...in Any Sport
REMOVE athlete from play
REFER to medical provider
REST no sports, no texting/TV
RETURN only with doctor's OK
Source: Children's Hospital Boston, Sports Concussion Clinic